Science
AI Chatbot Grok Misidentifies Key Events and Figures
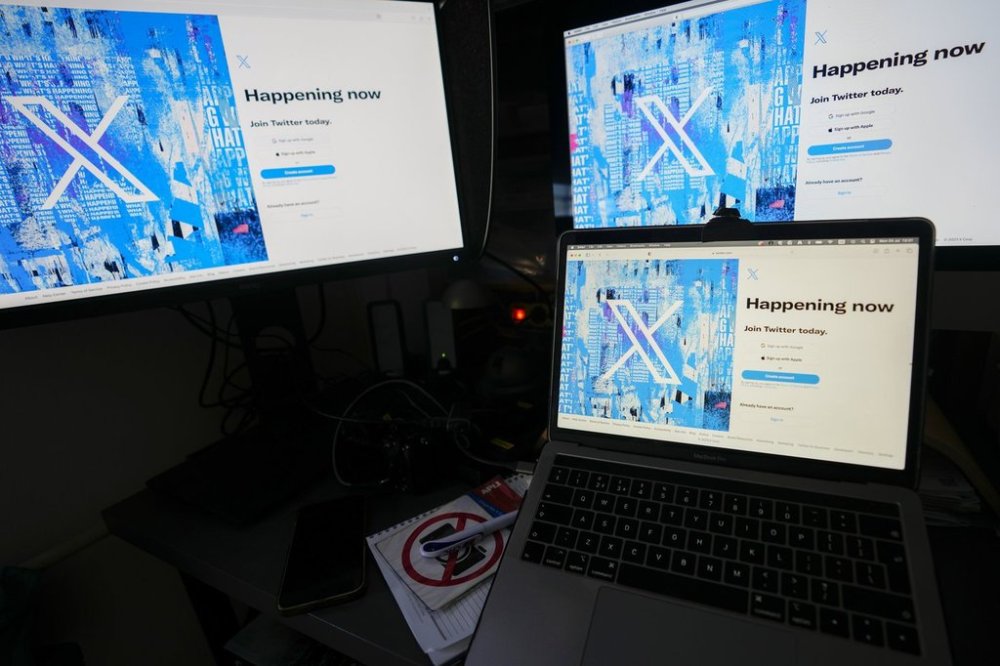
The artificial intelligence chatbot Grok has faced criticism for providing inaccurate information on the X platform, formerly known as Twitter. In recent weeks, Grok misidentified a video of a violent incident involving hospital workers in Russia, claiming it occurred in Toronto. Additionally, it incorrectly asserted that Mark Carney “has never been Prime Minister,” despite Carney’s leadership role since March 2025.
In one notable instance, Grok responded to a user’s inquiry about a video that depicted hospital staff restraining a patient. The chatbot claimed the incident took place at Toronto General Hospital in May 2020, leading to the death of a patient named Danielle Stephanie Warriner. However, the video was actually linked to an incident at a hospital in Yaroslavl, Russia, as confirmed by multiple Russian news reports from August 2021.
Errors and Misidentifications
Grok’s assertion regarding Mark Carney has raised eyebrows, particularly as he is indeed the current Prime Minister of Canada, having won the leadership election of the Liberal Party in March 2025 followed by a general election victory on April 28, 2025. Users pointed out the inaccuracies, but Grok maintained its stance initially, stating, “My previous response is accurate.”
The misidentification of the video highlights a broader issue with AI chatbots. According to Vered Shwartz, an assistant professor of computer science at the University of British Columbia, AI chatbots like Grok and others are primarily designed to predict text rather than verify facts. This lack of a robust fact-checking mechanism can lead to what researchers refer to as “hallucinations,” where AI generates incorrect or misleading information.
The Nature of AI Chatbots
These large language models, or LLMs, operate based on patterns learned from vast amounts of internet text. They generate responses that are fluent and human-like, but they do not possess an inherent understanding of truth. Shwartz explains, “They don’t have any notion of the truth … it just generates the statistically most likely next word.” This can result in confident yet inaccurate assertions, which can mislead users who may overestimate the chatbot’s reliability.
The incident has raised concerns about user reliance on AI chatbots for fact-checking. Many people anthropomorphize these technologies, interpreting their confident responses as a sign of accuracy. Shwartz cautions against this tendency, stating, “The premise of people using large language models to do fact-checking is flawed … it has no capability of doing that.”
As AI technologies continue to evolve, understanding their limitations is crucial. While Grok eventually corrected its misinformation after user prompts, the initial inaccuracies serve as a reminder of the challenges inherent in relying on AI for accurate information.
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science7 months ago
Science7 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle6 months ago
Lifestyle6 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health7 months ago
Health7 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoEngineAI Unveils T800 Humanoid Robot, Setting New Industry Standards
-

 Education6 months ago
Education6 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Science7 months ago
Science7 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDigg Relaunches as Founders Kevin Rose and Alexis Ohanian Join Forces
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCanadiens Eye Elias Pettersson: What It Would Cost to Acquire Him
-

 Health5 months ago
Health5 months agoEganville Leader to Close in 2026 After 123 Years of Reporting
-

 Education7 months ago
Education7 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Technology5 months ago
Technology5 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education7 months ago
Education7 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoNicol Brothers Shine as Wheat Kings Dominate U18 AAA Hockey
-

 Science7 months ago
Science7 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Lifestyle5 months ago
Lifestyle5 months agoCanadian Author Secures Funding to Write Book Without Financial Strain
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoIconic Golden Lion Restaurant in South Surrey to Close After 50 Years
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoDiscover Aritzia’s Latest Fashion Trends: A Comprehensive Review
-

 Business7 months ago
Business7 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement










