Science
Health Systems Boost Safety and Savings with Pharmacy Interventions
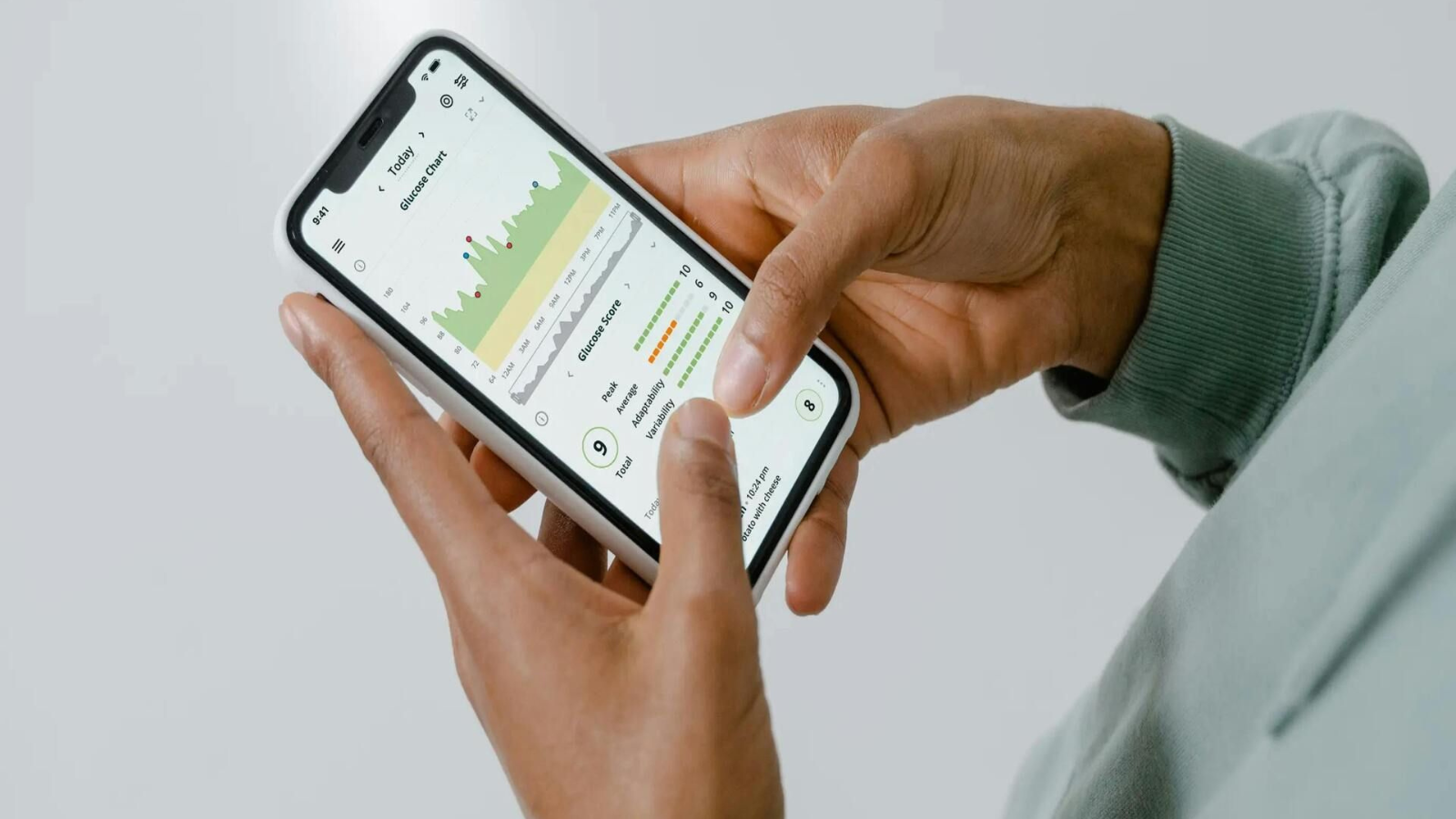

In the current healthcare landscape, organizations face the dual challenge of maintaining financial sustainability while enhancing patient safety and clinical outcomes. A promising solution lies in the strategic implementation of pharmacy intervention programs, which can effectively address these critical priorities. Recent insights highlight how health systems and payers can leverage these interventions to achieve significant cost savings and enhance patient care.
Understanding the Importance of Clinical Pharmacy Interventions
Medication-related issues remain a leading cause of preventable patient harm, contributing to increased healthcare costs. Challenges such as drug interactions, dosing errors, and non-adherence pose substantial risks. Clinical pharmacists, working collaboratively with physicians and care teams, play an essential role in mitigating these risks at various points in patient care.
Research underscores the effectiveness of these interventions. For instance, in an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) setting, the acceptance rate of recommendations from clinical pharmacists exceeded 90%, leading to safer prescribing practices and enhanced cost efficiency. Additionally, a systematic review conducted in Iran revealed that pharmacist-led initiatives significantly improved medication protocols and reduced errors. Various studies across multiple healthcare environments have also shown reductions in hospital readmissions and adverse drug events, affirming the efficacy of this model.
Key Components of a Successful Pharmacy Intervention Program
To maximize the potential of pharmacy intervention strategies, organizations should focus on four foundational pillars:
1. **Risk-Driven Targeting**: Not all patients or medications present equal opportunities for intervention. Initial efforts should concentrate on high-risk areas, including polypharmacy in complex patients, high-cost specialty therapies, and critical therapeutic classes such as anticoagulants and oncology agents.
2. **Integration into Care Workflows**: It is crucial for pharmacists to be actively involved in clinical rounds, case reviews, and care planning. Their presence fosters collaboration and trust among healthcare providers, enhancing the acceptance of their recommendations.
3. **Data and Analytics**: Tracking and analyzing every intervention is essential. This includes categorizing issues such as dosing errors or therapy duplications and quantifying their impact on clinical outcomes and cost avoidance. Robust analytics can help identify areas for improvement and demonstrate return on investment over time.
4. **Ongoing Training and Governance**: Clinical pharmacists require continuous education, clear guidelines, and collaborative governance structures that empower them to make evidence-based decisions. Shared accountability with physicians further promotes the adoption of interventions.
Implementation of these strategies can begin with a focused pilot program targeting a specific chronic condition, such as diabetes or heart failure, or a particular service line like discharge transitions. Defining clear intervention protocols and integrating access to clinical data can streamline the process. Establishing workflow touchpoints for pharmacists within care teams can significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Monitoring and quantifying results is vital. Tracking metrics such as acceptance rates and cost avoidance allows for iterative improvements and scaling successful practices across various populations and care settings.
As healthcare delivery continues to shift towards value-based models, the integration of clinical pharmacy interventions is becoming a strategic necessity. By effectively aligning these programs, organizations can enhance patient safety, improve clinical outcomes, and achieve substantial cost savings, ultimately reinforcing the sustainability of care networks.
For further insights on deploying and scaling pharmacy intervention programs, additional resources are available for organizations seeking to enhance their healthcare delivery systems.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBlue Jays Shift José Berríos to Bullpen Ahead of Playoffs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169