Health
Experts Warn of Rising Threat from Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
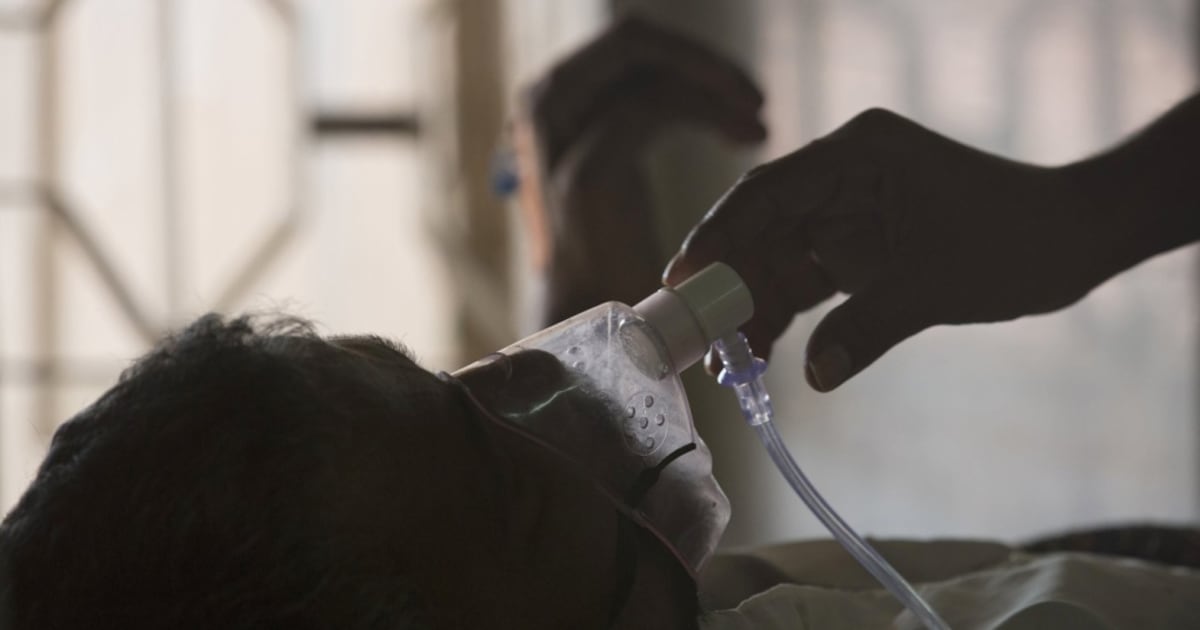
Drug-resistant organisms are increasingly challenging one of humanity’s most vital health measures: antibiotics. In an interview with CTVNews.ca, infectious disease expert Dr. Isaac Bogoch emphasized that these organisms are already present in Canada. His comments follow a report by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which issued a stark warning about the spread of what they termed “nightmare bacteria.”
Antibiotics have proven to be life-saving, but their overuse poses significant risks. “We need to have appropriate stewardship over them,” Dr. Bogoch said, noting that antibiotics are “used and abused” daily across various sectors. The term “nightmare bacteria” refers to pathogens that have evolved to resist antibiotics, complicating treatment for medical professionals.
The mechanism behind this resistance is concerning. When bacteria are exposed to antibiotics but survive the treatment, they can adapt and become resistant to the drugs. “We know the bacteria can mutate and change in such a way where the antibiotics are no longer lethal,” Dr. Bogoch explained. He described the ongoing struggle as an “arms race,” where new antibiotics are developed but bacteria continuously adapt. “We’re going to lose the arms race every time,” he warned.
One of the primary drivers of antibiotic resistance is the global agriculture industry. Dr. Bogoch pointed out that approximately 70 percent of antibiotic use occurs in agriculture, particularly in livestock such as pigs, sheep, and fish. This practice not only helps animals grow larger but also contributes to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance.
The Interconnectedness of Human and Animal Health
Dr. Bogoch stressed the importance of the “One Health” concept, which recognizes that human, animal, and environmental health are interlinked. As noted by the World Health Organization, the health of humans, domestic and wild animals, plants, and ecosystems are closely connected. Over-reliance on antibiotics in livestock can lead to the development of resistant organisms, which can then transfer to humans.
The implications of antibiotic resistance are severe, particularly for diseases that can evolve, such as tuberculosis (TB) and HIV. Dr. Bogoch highlighted that TB alone kills approximately one million people annually. In 2023, the World Health Organization reported a death toll from TB of 1.25 million, with nearly 11 million people infected worldwide. Drug-resistant strains of TB present significant treatment challenges, especially in regions lacking advanced medical facilities.
In Canada, public health data indicated 2,217 cases of TB in 2023, with over 10 percent of these cases classified as drug-resistant. Dr. Bogoch expressed concern over the ability of TB to evolve into resistant strains, particularly the multiple drug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) variants. “Many of the cases are in low-resource settings or may involve delays in diagnostics,” he noted, emphasizing the challenges in accessing timely treatment for patients.
Global Efforts to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
Efforts to address this pressing issue are underway, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where the burden of TB is especially high. The World Health Organization has set a target to end the TB epidemic by 2030, as part of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. In Canada, the Public Health Agency reported that TB drug resistance in 2023 remained low and consistent with overall trends. The agency collaborates with federal, provincial, territorial governments, and Indigenous partners to work towards the elimination of TB, promoting a united front to combat this global health threat.
Dr. Bogoch’s insights highlight the urgent need for sustainable antibiotic use and robust public health measures. As the fight against antibiotic resistance continues, coordinated efforts across human and animal health sectors will be essential in safeguarding future generations from the threats posed by these evolving pathogens.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBlue Jays Shift José Berríos to Bullpen Ahead of Playoffs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169