Science
New AI Model Revolutionizes Atrial Fibrillation Treatment Recommendations
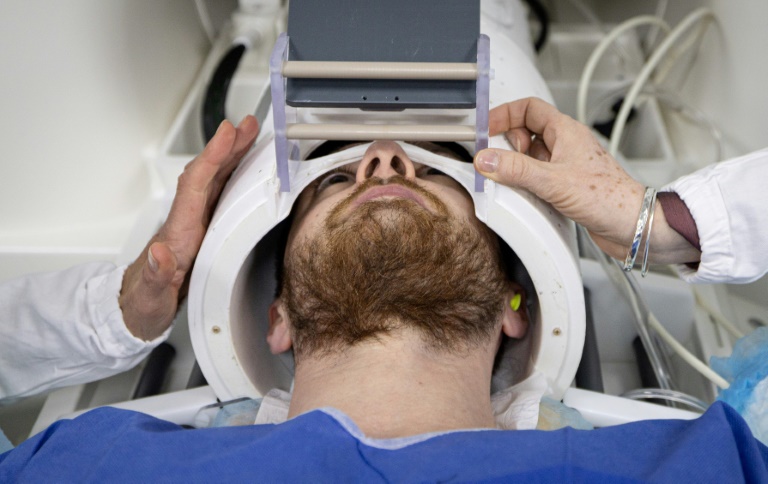
Researchers at Mount Sinai have developed a groundbreaking AI model that could significantly change treatment protocols for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). This innovative model offers personalized treatment recommendations, addressing the urgent need for individualized care in a condition that affects approximately 59 million people globally.
Atrial fibrillation is characterized by irregular heart rhythms, which can lead to stagnant blood flow and the formation of clots. These clots pose a risk of stroke if they travel to the brain. Traditionally, anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are prescribed to mitigate this risk. However, such treatments can also lead to serious complications, including major bleeding events. The new AI model aims to refine these treatment decisions, potentially recommending against anticoagulant therapy for nearly half of AF patients who would typically receive it under standard guidelines.
Individualized Treatment Framework
The AI model represents a significant advancement in precision medicine, moving beyond the one-size-fits-all approach prevalent in current clinical practice. By analyzing comprehensive electronic health records, including data from 1.8 million patients across 21 million doctor visits, 82 million notes, and 1.2 billion data points, the model assesses individual patient characteristics and risk factors.
Specifically, it evaluates the likelihood of stroke occurrence against the potential for major bleeding, thus providing a patient-level risk estimate. This tailored approach contrasts sharply with existing clinical tools that offer average risk assessments for populations rather than for individual patients. The model generates a net-benefit recommendation, guiding clinicians in making informed decisions based on the unique clinical features of each patient.
Robust Validation and Potential Impact
To validate its effectiveness, researchers tested the AI model within the Mount Sinai Health System, analyzing data from 38,642 patients. Additionally, external validation was conducted using publicly available datasets, which included 12,817 patients from Stanford University. The results indicated that the model’s recommendations aligned with strategies to minimize both stroke and bleeding risks.
The implications of this study extend beyond individual patient care. By potentially reclassifying around half of AF patients as unsuitable for anticoagulant therapy, the model could reshape treatment landscapes on a global scale. This shift could lead to reduced healthcare costs and improved patient safety, highlighting the necessity for advanced analytics in clinical decision-making.
The research is pioneering not only as the first individualized AI model focused on AF treatment but also as a significant step towards enhancing patient outcomes through technology. As the healthcare sector increasingly embraces innovations like this, the AI model from Mount Sinai stands as a promising example of how data-driven approaches can transform medical practices and patient care in the long term.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoBlue Jays Shift José Berríos to Bullpen Ahead of Playoffs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169










