Science
Google and UC Riverside Launch UNITE to Combat Deepfake Threats
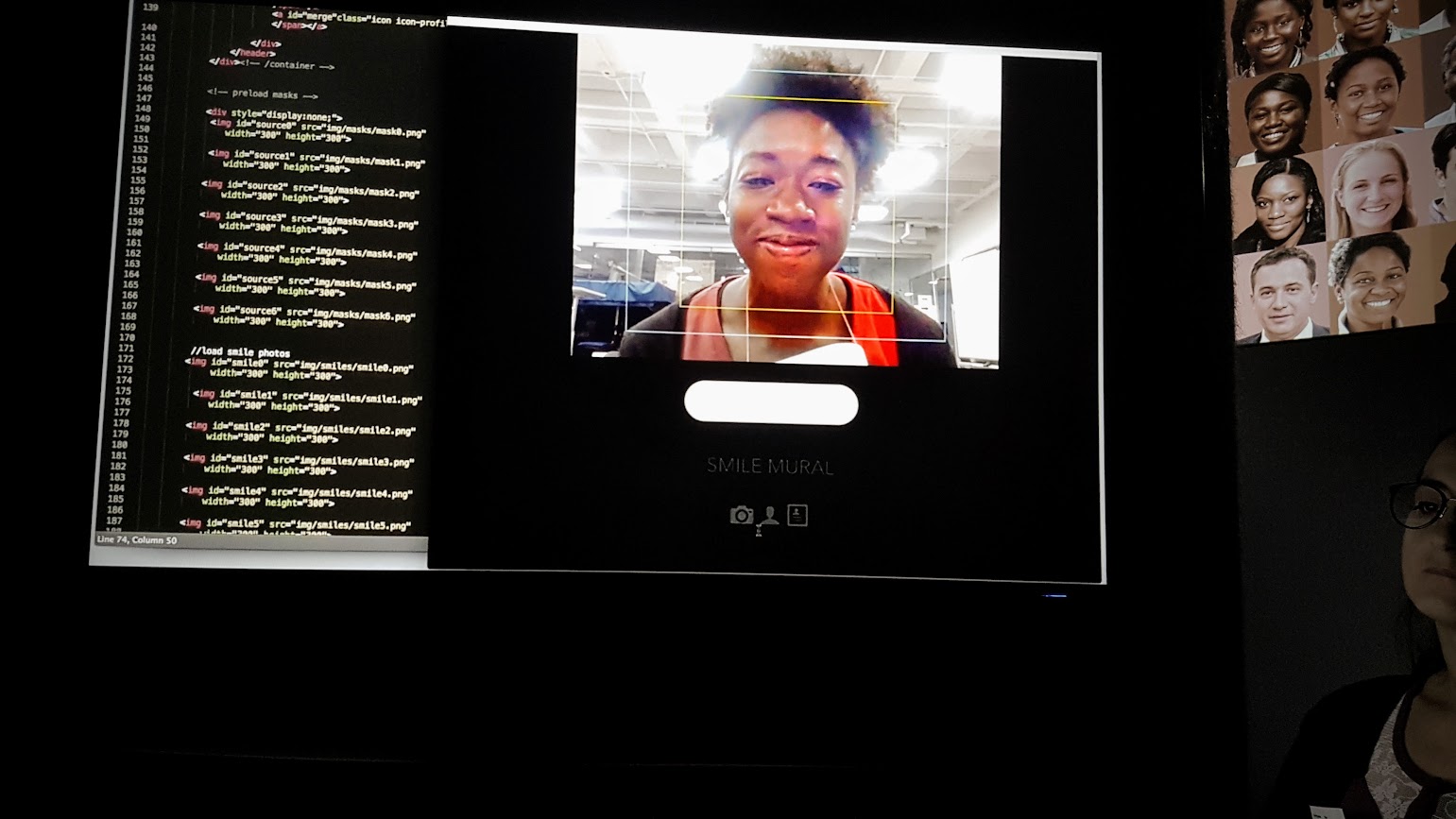
Researchers from the University of California – Riverside have partnered with Google to develop a new technology, named the Universal Network for Identifying Tampered and synthEtic videos (UNITE), aimed at combating the rising menace of deepfakes. This innovative system is designed to detect manipulated videos, even when facial features are not visible, addressing a significant limitation of existing detection tools.
As the production of AI-generated videos becomes increasingly sophisticated, the potential for misinformation grows. Deepfakes, a combination of “deep learning” and “fake,” are videos, images, or audio clips created using artificial intelligence that closely mimic real content. While some may use this technology for entertainment, it has been increasingly exploited to impersonate individuals and mislead the public.
Addressing Limitations in Detection Technologies
Current deepfake detection systems face challenges, particularly when there are no faces present in the footage. This gap highlights the need for a more versatile approach to identifying disinformation. Altering background scenes can distort reality just as effectively as creating phony audio, necessitating a tool that can analyze beyond facial content.
UNITE utilizes advanced techniques to identify forgeries by examining complete video frames, including backgrounds and motion patterns. This comprehensive analysis makes it the first technology capable of detecting synthetic or manipulated videos without relying solely on facial recognition.
The system employs a transformer-based deep learning model to scrutinize video clips for subtle spatial and temporal inconsistencies. These inconsistencies, often overlooked by previous detection systems, provide valuable clues about the authenticity of the content. Central to UNITE’s architecture is a foundational AI framework known as Sigmoid Loss for Language Image Pre-Training (SigLIP), which enables the extraction of features that are not tied to specific individuals or objects.
A novel training methodology called “attention-diversity loss” encourages the model to evaluate multiple visual regions within each frame. This approach prevents the system from focusing exclusively on facial elements, allowing for a more holistic analysis of the video content.
Significance of UNITE in the Current Landscape
The collaboration with Google has granted the researchers access to extensive datasets and computational resources, essential for training the model on a diverse range of synthetic content. This includes videos generated from both text and still images, formats that typically challenge existing detectors. The outcome is a universal detection tool capable of identifying a spectrum of forgeries, from simple facial swaps to entirely synthetic videos that do not contain any real footage.
The introduction of UNITE comes at a critical time when text-to-video and image-to-video generation tools are becoming widely accessible. These AI platforms enable almost anyone to create convincing videos, which poses serious risks to individuals, institutions, and potentially democratic processes in various regions.
The researchers presented their findings at the 2025 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) in Nashville, U.S. Their paper, titled “Towards a Universal Synthetic Video Detector: From Face or Background Manipulations to Fully AI-Generated Content,” details UNITE’s architecture and innovative training methods.
As the landscape of digital content continues to evolve, technologies like UNITE will be crucial in helping newsrooms, social media platforms, and the public discern truth from fabrication, safeguarding the integrity of information in an increasingly complex digital world.
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-
 Technology1 month ago
Technology1 month agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDiscover the Relaxing Charm of Tiny Bookshop: A Cozy Gaming Escape