Science
Discoveries in Science: Spaghetti, Snakes, and Martian Mysteries

Recent scientific research has unveiled a variety of intriguing findings, ranging from the unique microstructures of pasta to the striking speed of snake bites. These studies, gathered in a monthly roundup, highlight significant advancements across diverse fields, including archaeology, planetary science, and food technology.
Unraveling the Mystery of Spaghetti
A study published in the journal Food Hydrocolloids explores the microstructural differences between regular and gluten-free spaghetti. Researchers found that the gluten matrix in traditional pasta provides enhanced resistance to structural degradation during cooking. The analysis utilized small-angle x-ray scattering and small-angle neutron scattering to compare both types of pasta, revealing that the addition of salt not only enhances flavor but also fortifies this gluten network.
The implications of this research could lead to the development of gluten-free alternatives that better mimic the taste and texture of their gluten-containing counterparts, addressing the rising demand among those with gluten intolerance.
Snake Strikes Captured in High Definition
In a groundbreaking study, researchers at Monash University investigated the striking capabilities of 36 snake species, revealing the remarkable speed at which these reptiles can bite. The findings, published in the Journal of Experimental Biology, showcased snakes striking in as little as 60 microseconds, with vipers leading the pack by accelerating up to 710 m/s².
The researchers utilized high-speed cameras to capture over 100 individual strikes, providing insights into the varied biting techniques employed by different species. This research not only enhances our understanding of snake behavior but also holds potential implications for medical and pharmaceutical applications involving snake venom.
Martian Gullies: New Insights into Planetary Processes
A study in the journal Geophysical Research Letters sheds light on the formation of gullies on Mars, suggesting that seasonal deposition and sublimation of CO2 ice play a critical role. Earth scientist Lonneke Roelofs from Utrecht University conducted experiments simulating Martian conditions, revealing how CO2 ice can create gullies as it sublimates and moves down dune slopes.
This research contributes to the ongoing debate regarding the planet’s climatic history and its potential for past habitability, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of Martian geology.
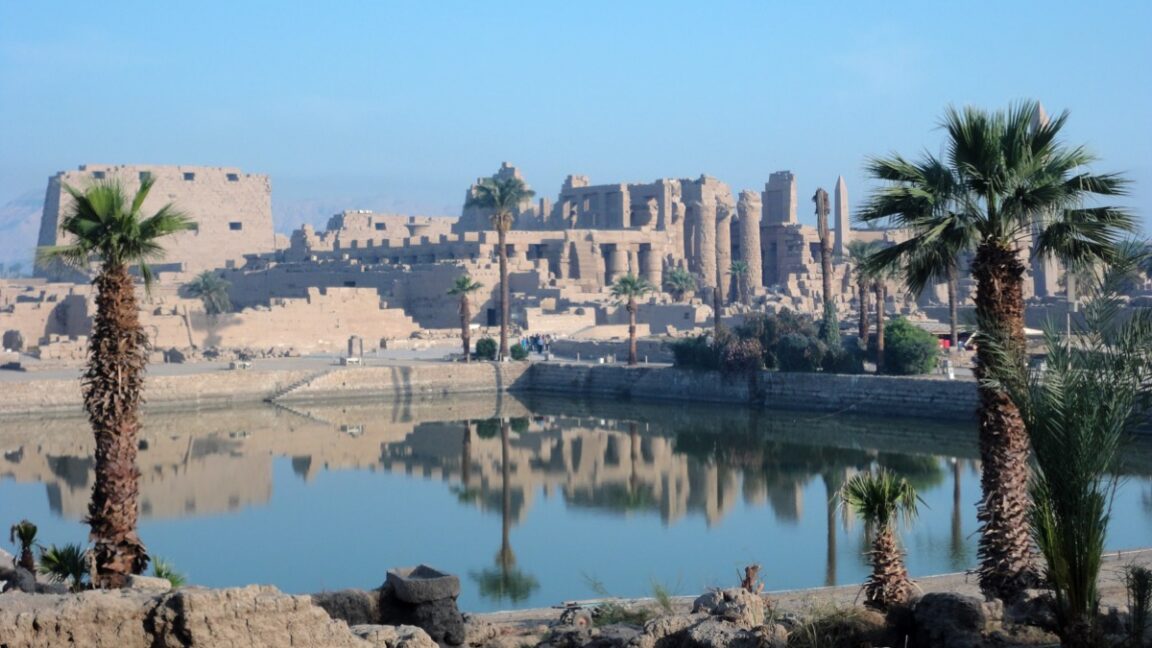
Discovering the Origins of Karnak Temple
Archaeological investigations at Egypt’s Karnak Temple complex, located near Luxor, have provided new insights into its origins. A comprehensive geological survey published in Antiquity indicates that the temple’s earliest permanent settlement emerged between 2591 and 2152 BCE, following regular flooding from the Nile.
The study analyzed sediment cores and ceramic fragments, suggesting that the Temple’s location was deliberately chosen due to its connection to ancient creation myths. Co-author Ben Pennington, a geoarchaeologist at the University of Southampton, noted the significance of the site in relation to the Egyptian god Ra-Amun.
Exploring the Ancient Art of Finger Flutings
In a novel approach to archaeology, digital archaeologist Andrea Jalandoni of Griffith University has applied machine learning to study finger flutings, some of the oldest known examples of prehistoric art. Her research, published in Scientific Reports, involved recreating finger flutings in both virtual reality and real clay environments to evaluate the accuracy of machine learning classifications.
While the results varied, the study achieved up to 84% accuracy in differentiating between flutings made by men and women, suggesting potential applications in cultural heritage management. Jalandoni emphasized the importance of this research for granting access to culturally significant sites.
These diverse studies illustrate the dynamic nature of scientific inquiry, revealing new perspectives on both ancient and contemporary phenomena. As researchers continue to explore these fascinating topics, the implications for understanding our world—and beyond—remain profound.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoBlue Jays Shift José Berríos to Bullpen Ahead of Playoffs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169