Science
Discovering Ancient Mysteries: Science Stories You Should Know

A variety of intriguing scientific discoveries have emerged recently, shedding light on everything from ancient Egyptian architecture to the mechanics of snake bites. These findings, explored in studies published in reputable journals, highlight the diverse and often unexpected nature of research in the scientific community.
Unlocking the Secrets of Spaghetti
A recent study published in the journal Food Hydrocolloids examined the microstructural differences between regular and gluten-free spaghetti. Researchers used advanced techniques like small-angle x-ray scattering to analyze the gluten matrix of both types of pasta. They discovered that the gluten matrix in traditional spaghetti provides better structural integrity. Interestingly, adding salt during cooking further enhances this matrix, contributing to a superior taste and texture. This research could pave the way for improved gluten-free alternatives that better mimic the qualities of regular pasta.
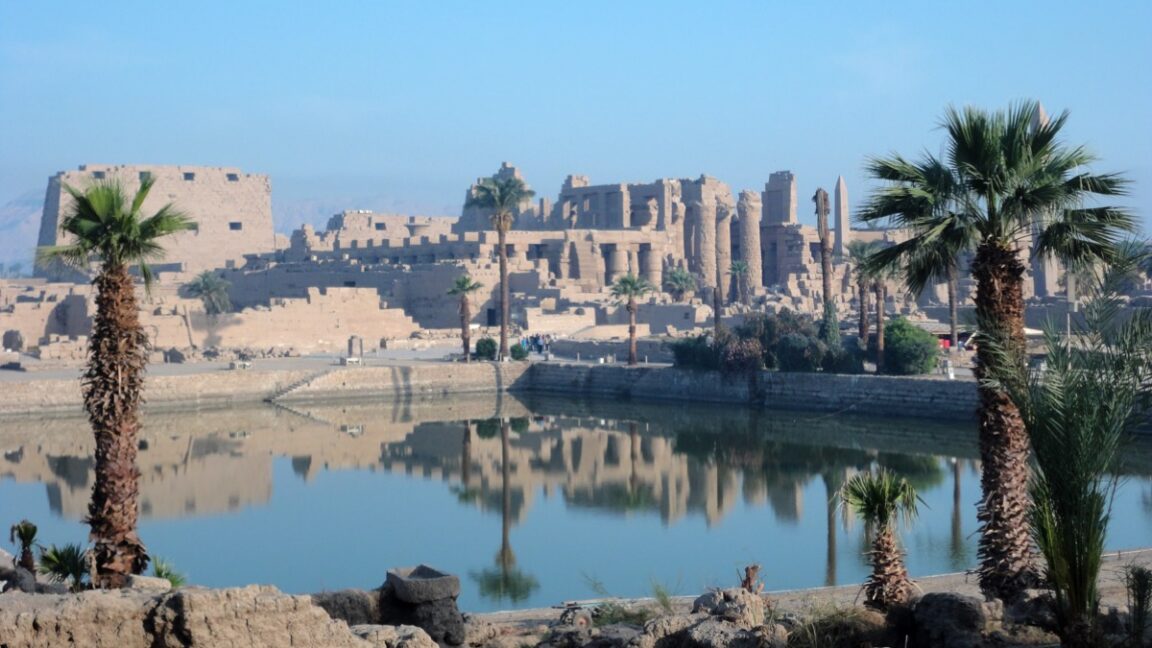
Insights into Egypt’s Karnak Temple
The origins of the Karnak Temple complex in Egypt, located near Luxor, have been clarified through a comprehensive geological survey published in Antiquity. The study, which involved analyzing sediment cores and ceramic fragments, suggests that the site was regularly flooded by the Nile around 2520 BCE. This flooding likely led to the establishment of the earliest permanent settlement at Karnak between 2591 and 2152 BCE. Co-author Ben Pennington, a geoarchaeologist at the University of Southampton, noted that the temple’s location may have been chosen to align with Egyptian creation myths, further enhancing its historical significance.
Understanding Martian Gullies
Research published in Geophysical Research Letters has provided new evidence regarding the formation of gullies on the surface of Mars. The study, led by earth scientist Lonneke Roelofs from Utrecht University, suggests that these features are primarily created by the seasonal sublimation of carbon dioxide ice rather than ancient water flows. Through experiments simulating Martian conditions, Roelofs demonstrated how CO2 ice can create gullies when it melts and moves down slopes, offering insights into Mars’ geological processes.
Capturing the Speed of Snake Strikes
Researchers at Monash University recently achieved a significant breakthrough in understanding snake strikes. Their study, published in the Journal of Experimental Biology, examined 36 snake species and utilized high-speed cameras to capture their biting techniques. Findings revealed that vipers strike at incredible speeds, with the blunt-nosed viper reaching an acceleration of 710 m/s² and biting within just 22 microseconds. This research not only highlights the diversity of snake behavior but also provides valuable insights into their predatory strategies.
Computational Proof in Boggle
In an unusual intersection of mathematics and gaming, software engineer Dan Vanderkam has developed a computational proof for the highest-scoring Boggle board configuration. His study, shared in a preprint on the physics arXiv, identifies a configuration yielding a remarkable score of 3,625 points, with over 1,000 possible words, including the longest word “replastering.” Vanderkam’s innovative approach to grouping board patterns allowed him to discard less optimal configurations, showcasing the application of mathematical techniques in recreational gaming.
Machine Learning and Ancient Art
Lastly, a study published in Scientific Reports explores the potential of machine learning to identify the ancient artists behind finger flutings found in prehistoric caves. Conducted by digital archaeologist Andrea Jalandoni at Griffith University, the research involved creating finger flutings in both virtual reality and real clay. The results indicated that while the virtual reality images yielded unreliable classifications, the clay-based images achieved close to 84 percent accuracy. This highlights the promise of machine learning in archaeological research, although further refinement is needed for practical applications.
These diverse stories not only enrich our understanding of science but also illustrate the broad spectrum of research currently taking place across various fields. From pasta to ancient temples, these findings remind us of the endless curiosity driving scientific inquiry.
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-
 Technology4 weeks ago
Technology4 weeks agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology3 months ago
Technology3 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoArsanesia Unveils Smith’s Chronicles with Steam Page and Trailer










