Business
Netflix’s $72 Billion Bid for Warner Bros. Faces Antitrust Scrutiny
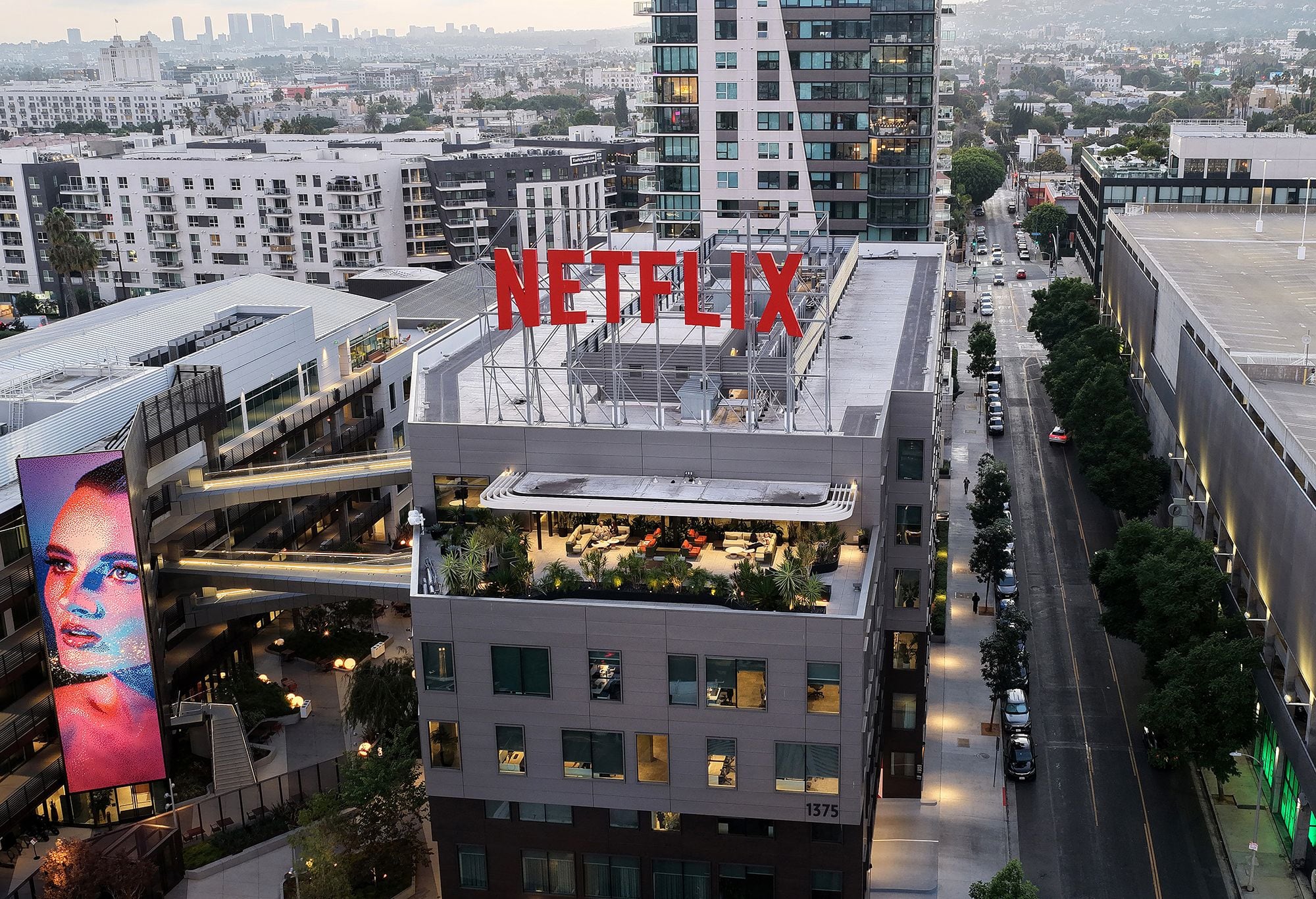

Netflix is making headlines with its ambitious bid of $72 billion to acquire Warner Bros. and HBO, a move that could reshape the media landscape. This proposed merger poses significant implications for the industry, particularly amidst evolving consumer behaviors influenced by tech giants like YouTube and TikTok. As the entertainment sector grapples with these changes, the deal raises pressing questions about competition and regulatory approval.
The potential acquisition is not just a corporate transaction; it represents a strategic effort by Netflix to consolidate its position in an increasingly competitive streaming market. By merging with Warner Bros. and HBO, Netflix aims to leverage Warner’s extensive intellectual property to create new content that may not be feasible for Warner Bros. Discovery alone. This could enhance HBO’s reach, attracting a more diverse audience and generating additional funds for high-quality productions.
Nevertheless, the merger is likely to attract intense scrutiny from antitrust regulators globally. Governments are particularly concerned about whether such a consolidation could diminish competition and adversely affect consumers. The proposed merger would unite two of the world’s largest streaming services, Netflix and HBO Max, at a time when subscription prices are rising due to slowed growth. This would push the combined market share beyond the 30% threshold that triggers regulatory investigations in the United States.
According to Herbert Hovenkamp, an antitrust law professor at the University of Pennsylvania, the deal “looks challengeable.” He notes that the concentration of the market raises concerns about price increases. The U.S. Department of Justice’s recent guidelines on antitrust, issued in 2023, signal a heightened approach to reviewing such mergers, a marked shift from previous administrations.
Political dynamics could further complicate the approval process. While the Republican Party has traditionally favored business-friendly policies, populist voices within the party, including Senator Josh Hawley and Senator Mike Lee, have expressed skepticism about the merger, calling for antitrust officials to take a closer look. Vice President JD Vance has also shown support for stricter enforcement of antitrust laws, which may influence negotiations.
International regulators, particularly in Europe, are expected to weigh in on the merger as both Netflix and Warner Bros. Discovery have substantial global operations. According to industry insiders, Paramount has advocated against the merger, suggesting that Netflix’s expansion could face significant regulatory hurdles.
As Netflix prepares its case, the company emphasizes its sophisticated algorithms and deep understanding of viewer preferences. If regulators perceive the merger as a means of enhancing efficiency and competition, it may receive a more favorable review. In contrast, if the focus is on growth and market dominance, the outcome could be less promising.
Doha Mekki, a former acting assistant attorney general for the DOJ’s antitrust division, highlights the importance of understanding Netflix’s motivations behind the merger. She notes that regulators will assess whether the acquisition would increase Netflix’s power over creators and consumers, potentially stifling innovation at Warner Bros. and HBO.
The impact on the workforce is another critical factor in the merger debate. The shift to streaming has already transformed Hollywood’s business model, resulting in shorter theatrical exclusivity periods and fewer jobs for theater workers, writers, and production staff. Unions, including the Writers Guild of America, have voiced strong opposition to the merger, fearing it could exacerbate job losses and reduce overall content diversity.
While Netflix asserts that the acquisition would create new opportunities for creators, labor advocates caution that the deal could further entrench a streaming-first model that diminishes competition and employment prospects. The Writers Guild stated, “The world’s largest streaming company swallowing one of its biggest competitors is what antitrust laws were designed to prevent.”
Although antitrust regulators typically focus on consumer harm, there is precedent for examining the effects of mergers on workers, as demonstrated by the DOJ’s successful challenge of Penguin Random House‘s proposed acquisition of Simon & Schuster. This case centered on how fewer publishing options could lead to lower advances for authors.
In conclusion, Netflix’s bid for Warner Bros. and HBO represents a pivotal moment for the future of media consolidation. As the regulatory landscape evolves, the outcome of this merger could set significant precedents for antitrust enforcement in the entertainment industry. The coming months will likely reveal whether Netflix can effectively navigate the complex web of competition concerns and political dynamics to secure its ambitious acquisition.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoBrandon University’s Failed $5 Million Project Sparks Oversight Review
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoMicrosoft Confirms U.S. Law Overrules Canadian Data Sovereignty
-

 Lifestyle3 months ago
Lifestyle3 months agoWinnipeg Celebrates Culinary Creativity During Le Burger Week 2025
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoMontreal’s Groupe Marcelle Leads Canadian Cosmetic Industry Growth
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoTech Innovator Amandipp Singh Transforms Hiring for Disabled
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoDragon Ball: Sparking! Zero Launching on Switch and Switch 2 This November
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoRed River College Launches New Programs to Address Industry Needs
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGoogle Pixel 10 Pro Fold Specs Unveiled Ahead of Launch
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoRocket Lab Reports Strong Q2 2025 Revenue Growth and Future Plans
-

 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoDiscord Faces Serious Security Breach Affecting Millions
-

 Education4 months ago
Education4 months agoAlberta Teachers’ Strike: Potential Impacts on Students and Families
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoChina’s Wukong Spacesuit Sets New Standard for AI in Space
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoNew SĆIȺNEW̱ SṮEȽIṮḴEȽ Elementary Opens in Langford for 2025/2026 Year
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoWorld of Warcraft Players Buzz Over 19-Quest Bee Challenge
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoNew Estimates Reveal ChatGPT-5 Energy Use Could Soar
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoDawson City Residents Rally Around Buy Canadian Movement
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoBNA Brewing to Open New Bowling Alley in Downtown Penticton
-
 Technology2 months ago
Technology2 months agoHuawei MatePad 12X Redefines Tablet Experience for Professionals
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoFuture Entertainment Launches DDoD with Gameplay Trailer Showcase
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoGlobal Launch of Ragnarok M: Classic Set for September 3, 2025
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoInnovative 140W GaN Travel Adapter Combines Power and Convenience
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBlue Jays Shift José Berríos to Bullpen Ahead of Playoffs
-

 Science4 months ago
Science4 months agoXi Labs Innovates with New AI Operating System Set for 2025 Launch
-

 Technology4 months ago
Technology4 months agoNew IDR01 Smart Ring Offers Advanced Sports Tracking for $169










